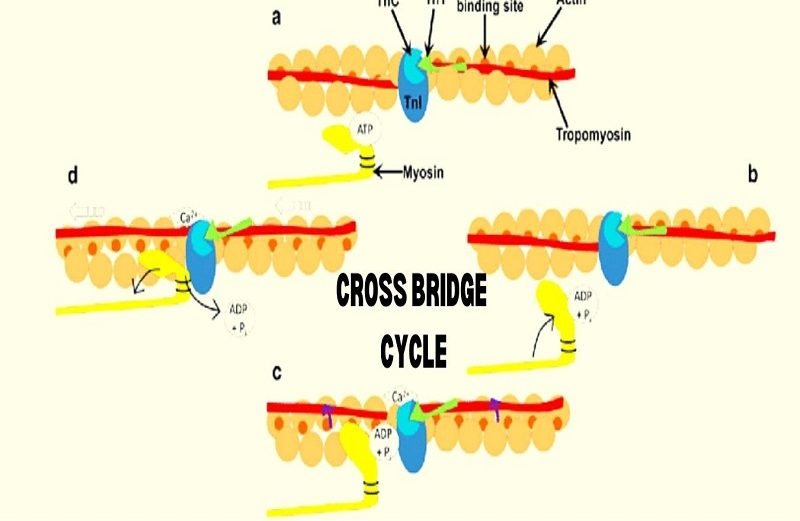
What Is The Role of Calcium In The Cross Bridge Cycle? To understand the Cross Bridge Cycle & its effect on muscle contraction, you require to be close with the ‘Contractile-Machinery’ that causes muscle shortening & the Sliding-Filament theory. To briefly recap, Muscle-Contraction occurs when the thin Filament, Actin, Slide past the Thick-Filament, myosin, This is essentially the Sliding-Filament theory. The mechanism that makes the Actin-Filaments slide past the myosin Cross Bridge Cycle in skeletal muscle, in brief, is as follows:
Remembering that a sarcomere is the extent of myofibril btw 2 z lines where myosin Cross Bridge Cycle in central & an Actin-Filament is both above & below the myofibril on every side of it, with its medial Side-Slightly overlapping myosin & its Lateral-Side joined firmly to the z line. Nerve impulse arrives at muscle, causing the release of calcium from the Sarcoplasmic-Reticulum of Muscle-Fibre
What Is The Role of Calcium In The Cross Bridge Cycle? Troponin is bound to tropomyosin which is attached to actin. When the tissue is at rest, tropomyosin is resting in such a situation, that it is covering the required sites for myosin heads on actin.
What Is The Role of Calcium In The Cross Bridge Cycle? Calcium bind to troponin. This makes it to undergo a conformational shift which pulls the tropomyosin it is joined out of its comfortable position, exposing binding sites for myosin heads on actin.
Myosin Cross Bridge Cycle heads covalently bind to the detected binding sites. The myosin head feels a conformational shift which pulls the actin along. What Is The Role of Calcium In The Cross Bridge Cycle? It then delivers the actin, turns to its original conformation, extending out sideways again & forms a bind with another Actin-Binding site that is further along the actin & closer to the Z-Line. This repeated motion is what causes the sliding of the Actin-Filament Past-Myosin.
What Is The Role of Calcium In The Cross Bridge Cycle? Cross bridge cycling refers especially to the action of the Cross Bridge Cycle, that being the head & hinge region of the Myosin-Filament. It is essentially acting as a bridge when the head is Covalently-Bonded to actin, & this bridge is continuously being formed & broken during muscle contraction-the Cross bridge cycling is being cycled, & bit is this action that is allowing for the filaments to slide the way they do.
The Cross Bridge cycle can be crushed down as follows:
What Is The Role of Calcium In The Cross Bridge Cycle? Hydrolysis of ATP to ADP & Pi, with products still Covalently-Bonded to myosin, cause it to enter an Energised-State. Cross bridge cycling binds to actin. It undergoes a Conformational-Change. ADP & Pi are released. You then get a Power-Stroke (ie Cross bridge cycling moves, pulling Actin-Along which causes the Power-Stroke).
In this article, we at BestComfortBike will give a complete guide on the important topic of What Is The Role of Calcium In The Cross Bridge Cycle. You will be grateful that you have read this article & choice the best Idea for You! Let’s get started!
Editor’s Recommendations
- WHAT IS A CROSS BRIDGE CYCLE
- Best Trail Running Shoes For Women
- Best Triathlon Cycling Shoes
- Touring Cycling Shoes
- Winter Mountain Bike Shoes
- BCB Bicycle Handlebar Grips Fit Many Standard Bikes
- BCB Mountain Bicycle Soft Rubber Grips Fit Many Standard Bikes
- BCB Bicycle Grips For BMX/Road Mountain/Boys And Girls Kids Bikes
- BCB BMX & Mountain Bike Handlebar Grips Non-Slip Soft
- BCB Mountain Bike Handlebar Grips, Two Colour